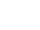
Overview
A carbon footprint project is a method and calculation process that measures and evaluates the greenhouse gas (mainly carbon dioxide) emissions produced by an individual, organization or product during a specific time period. It aims to understand and quantify the contribution of human activities to climate change and provide guidance for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
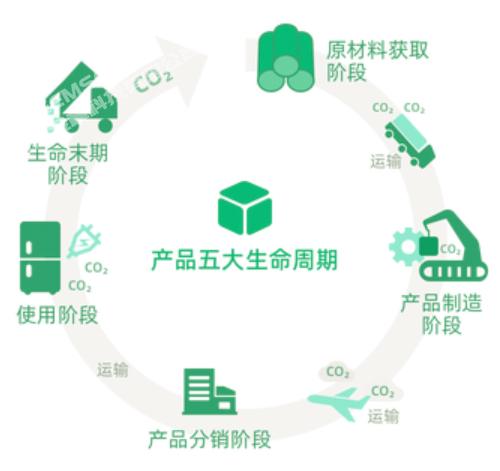
Carbon footprint projects usually include the following steps:
Defining the Scope: Clarify the scope of the project and determine the emission sources that need to be calculated and the types of activities covered. This can include direct emissions (e.g. energy use, transportation, etc.) and indirect emissions (e.g., supply chains, waste management, etc.).
Data collection: Collect project-related data, such as energy usage, transportation mileage, waste generation, etc. These data can come from the company's internal records, data provided by suppliers, industry standard data, etc.
Emission calculation: Based on the collected data, use carbon footprint calculation methods and formulas to calculate the greenhouse gas emissions generated by each activity. Calculations are usually expressed in terms of carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2e), which converts the impact of other greenhouse gases into units equivalent to carbon dioxide.
Data analysis and interpretation: Analyze and interpret the calculated emission data to understand the contribution of each activity to the total emissions, and identify high-carbon emission links and potential emission reduction opportunities. This can help businesses or organizations identify strategies and measures to reduce emissions.
Reporting and communication: Organize calculation and analysis results into reports or visualizations to communicate carbon footprint information to stakeholders in a clear and understandable way. This can include internal management and employees, as well as external partners, customers and investors.
Emission reduction actions: Develop and implement emission reduction plans and measures based on analysis results and perceived emission reduction opportunities. This can include energy efficiency improvements, renewable energy procurement, supply chain optimization, waste management improvements, and more.
Monitoring and reporting: Continuously monitor and evaluate the effects of emission reduction actions, regularly report emissions and emission reduction results, ensure the achievement of emission reduction targets and promote continuous improvement.
Through the carbon footprint project, individuals, organizations and governments can better understand their own greenhouse gas emissions, identify emission reduction priorities and opportunities, and promote sustainable development and actions to address climate change. In addition, the carbon footprint project also provides foundation and support for enterprises to establish an environmentally friendly image, meet policy requirements, and participate in the carbon market.
Program Features
Measurability: The carbon footprint project plan should have measurable characteristics, that is, it can accurately measure and calculate the carbon emissions of the organization or enterprise. By collecting and analyzing relevant data, the carbon emissions of each link can be determined and accurately measured.
Comprehensiveness: The carbon footprint project plan should comprehensively consider the carbon emissions of the organization or enterprise throughout the entire value chain. From raw material procurement, production and manufacturing, logistics and transportation to product use and waste disposal, all aspects should be taken into consideration to form full life cycle carbon emission data.
Standardization: Carbon footprint project plans should be based on national, industry or international standards to ensure consistency and comparability of carbon emission calculations and reporting. Follow uniform measurement methods and guidelines so that data from different organizations or businesses can be compared and evaluated with each other.
Transparency: Carbon footprint project plans should provide transparency of data and calculation processes to ensure data accuracy and verifiability. Relevant information should be publicly disclosed, including data sources, calculation methods and assumptions, to facilitate external review and supervision.
Refined: The carbon footprint project plan should be refined, that is, different departments, products or services can be calculated separately. This can help organizations or companies better understand the main sources of carbon emissions and formulate targeted emission reduction strategies and measures.
Practicality: The carbon footprint project plan should have practical and feasible characteristics and match the actual situation of the organization or enterprise. The plan should take into account factors such as technical feasibility, economic cost and resource constraints, and formulate practical emission reduction targets and measures.
Iteration: The carbon footprint project plan should have the characteristics of iterative improvement, that is, it can be adjusted and optimized based on data analysis and evaluation results. Periodically review and optimize the plan to gradually improve the accuracy and completeness of calculation methods and the effectiveness of emission reduction measures.
Integration: The carbon footprint project plan should be integrated with other relevant management systems and specifications, such as environmental management systems, sustainable development guidelines, etc. By combining it with the existing management framework, the comprehensive benefits of carbon management and emission reduction can be improved.
To sum up, the carbon footprint project plan should have the characteristics of measurable, comprehensive, standardized, transparent, refined, practical, iterative and integrated to ensure the accurate calculation and effective management of carbon emissions.
System Architecture
The system architecture of the carbon footprint solution can include the following core components:
Data collection and management: This component is responsible for collecting, storing and managing data related to carbon emissions. Data sources can include energy usage records, transportation data, production process data, etc. Collect data through sensors, monitoring equipment, enterprise information systems, etc., and store the data in a database or data warehouse for management.
Carbon emission measurement and calculation: Measure and calculate carbon emissions based on data collection. According to standardized calculation methods and guidelines, the data in each link is processed and converted to calculate carbon emissions. This may involve calculations of energy consumption, assessment of the impact of waste disposal, etc.
Data analysis and visualization: Analyze and visually present the calculated carbon emission data. Analyze the trends, main sources and potential influencing factors of carbon emissions through data analysis techniques and tools. At the same time, the analysis results are displayed in the form of charts, reports, etc., to visually present the carbon footprint data.
Emission reduction strategies and plans: Based on the results of data analysis, formulate targeted emission reduction strategies and plans. Based on the actual situation and goals of the organization or enterprise, design an emission reduction plan and formulate a corresponding action plan. Strategies may involve energy efficiency improvements, clean energy adoption, logistics optimization, etc.
Emission reduction implementation and management: This component is responsible for the implementation and management of emission reduction plans. Supervise the implementation of emission reduction measures, track emission reduction progress, and timely adjust and optimize emission reduction measures. Corresponding management systems need to be established to ensure that emission reduction measures can be effectively implemented and continuously improved.
Reporting and certification: Carry out carbon footprint reporting and certification according to relevant national or industry requirements. Prepare carbon footprint reports and report to relevant agencies in accordance with prescribed cycles. At the same time, if necessary, participate in relevant carbon emission certifications, such as ISO 14064, etc., to prove the compliance and credibility of the carbon footprint project.

System integration and support: In order to ensure the normal operation of the carbon footprint solution system, system integration and technical support are required. Integrate various components to ensure data transmission and sharing, and provide system stability and reliability. At the same time, we provide technical support and training to ensure the normal use of the system.
In addition, other components can also be considered based on specific needs, such as the traceability and verification of carbon footprint data, carbon trading platforms, etc., to further improve the system architecture of the carbon footprint solution. Overall, the system architecture integrates data collection, measurement, analysis, emission reduction, reporting, certification and other aspects to form a system for effective management and monitoring of carbon footprint, helping organizations or enterprises to quantify and manage carbon emissions.
Main Functions
The functions of the carbon footprint project include the following aspects:
Data collection and management: Provide data collection and management functions, including the input and recording of energy consumption, material use, industrial chain links, transportation and logistics and other related data. Data can be collected through manual entry, data import, or integrated with internal corporate systems and ensure data accuracy and completeness.

Carbon emission calculation: Provides carbon emission calculation function to calculate carbon emissions based on the collected data. According to different industries and standards, suitable calculation methods and formulas can be selected to calculate different types of carbon emissions such as direct emissions and indirect emissions.
Data analysis and reporting: It has data analysis and reporting functions, analyzes and interprets the calculated carbon emission data, and generates visual reports and charts. This helps decision-makers and stakeholders understand the carbon footprint of an enterprise or product and identify major sources of carbon emissions and potential emission reduction opportunities.
Formulation of carbon emission reduction measures: Supports the function of formulating carbon emission reduction measures and action plans. Based on the results of data analysis, it provides suggestions and guidance to help users formulate specific carbon emission reduction strategies and goals. It can combine industry best practices and policy requirements to provide users with functions such as feasibility assessment and risk analysis.
Implementation and monitoring: Provides implementation and monitoring functions to help users implement carbon emission reduction measures and monitor their implementation and effects. It can set key performance indicators (KPIs) and goals, track project progress, energy consumption, carbon emissions and other data, and provide timely reports and prompts so that users can adjust and improve measures in a timely manner.
Data security and privacy protection: Ensure data security and privacy protection. During the data collection, storage and transmission process, necessary security measures are taken, such as encryption, access rights control, etc., to protect users' data security and privacy.
User support and training: Provide user support and training functions, including operating guidance, training materials and technical support, etc., to help users become familiar with and correctly use the functions of the carbon footprint project, solve problems and improve usage effects.
Functional design needs to be carried out according to specific carbon footprint project needs and user characteristics. In the process of continuous improvement and optimization, the functions of the project must be gradually improved to achieve better carbon emission reduction effects and user experience.